By using this site you agree to the use of cookies by the company in accordance with the Privacy Policy
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, the steel sheet laser cutting machine has emerged as a pivotal technology, revolutionizing the way industries process metal materials. As noted by industry expert Dr. John Smith, a leading authority in advanced manufacturing technologies, "The steel sheet laser cutting machine not only enhances precision but also significantly reduces waste and operational costs." This statement underscores the profound impact of this technology on efficiency and sustainability in metal fabrication.
The steel sheet laser cutting machine operates by focusing a high-powered laser beam onto the surface of steel sheets, allowing for intricate designs to be cut with unparalleled accuracy. This process not only improves productivity but also enables manufacturers to meet the ever-growing demands for customization in various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. As industries continue to seek innovative solutions, the role of the steel sheet laser cutting machine will undoubtedly play a critical role in shaping the future of fabrication processes, making it an indispensable tool for manufacturers worldwide.
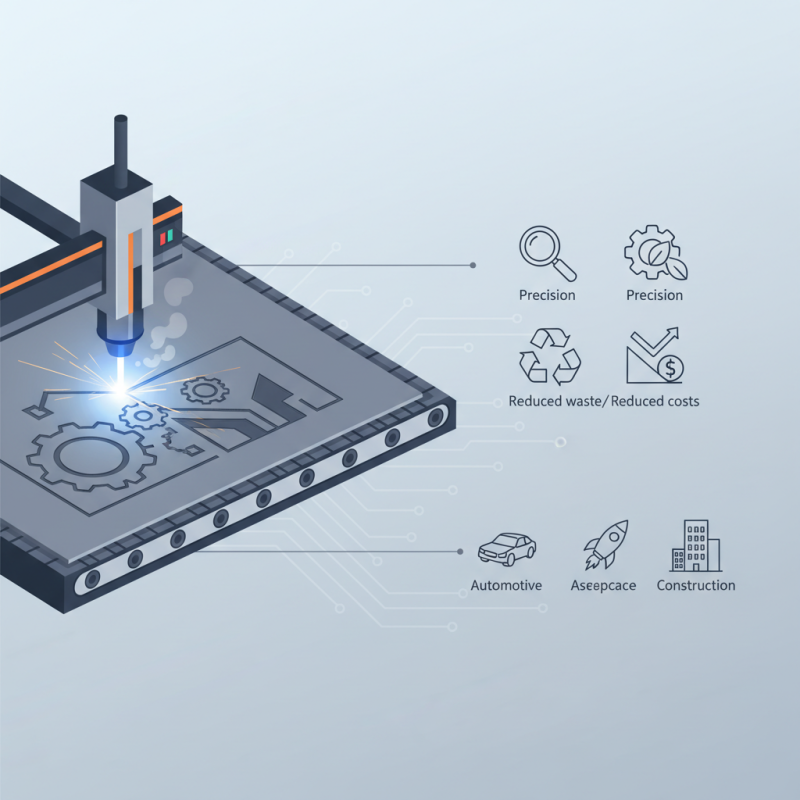
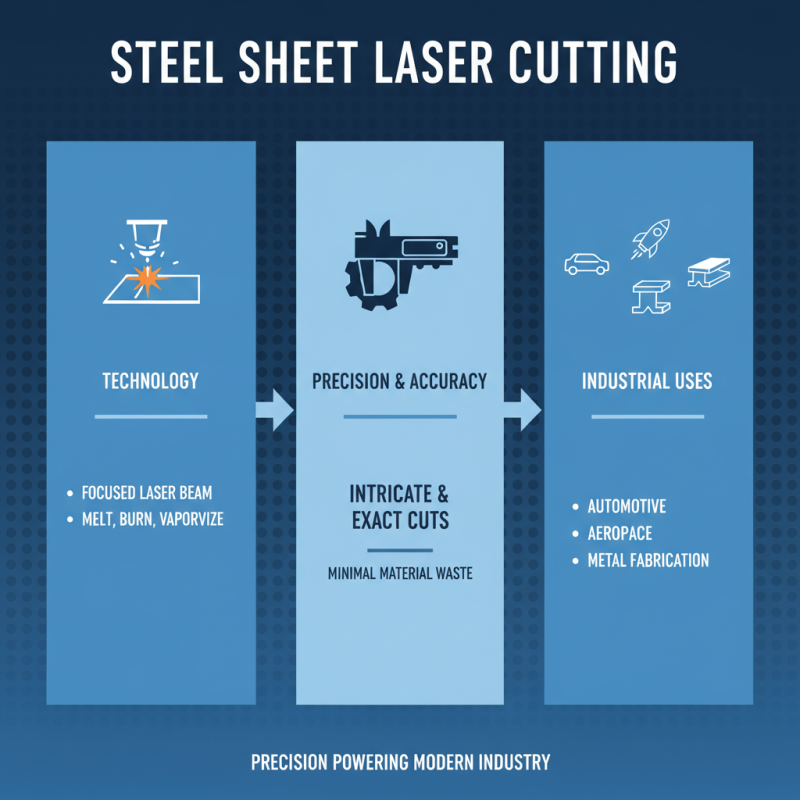
A steel sheet laser cutting machine is a sophisticated tool designed to cut steel sheets using focused laser beams. This technology leverages the precision of laser energy to melt, burn, or vaporize the steel material, enabling highly intricate and accurate cuts. Such machines are pivotal in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication, where precision is paramount.
The operation of a steel sheet laser cutting machine involves several steps. Initially, a laser generator produces a coherent beam of light, which is then directed through a series of mirrors and lenses to focus the beam onto the steel surface. As the concentrated laser hits the sheet, it raises the temperature of the steel to its melting point, creating a narrow kerf. Simultaneously, an assist gas, often oxygen or nitrogen, is blown through the cutting nozzle to aid in the cutting process by blowing away the molten steel and enhancing the speed and quality of the cut. This process allows for greater flexibility in design, enabling manufacturers to achieve complex shapes with minimal waste.
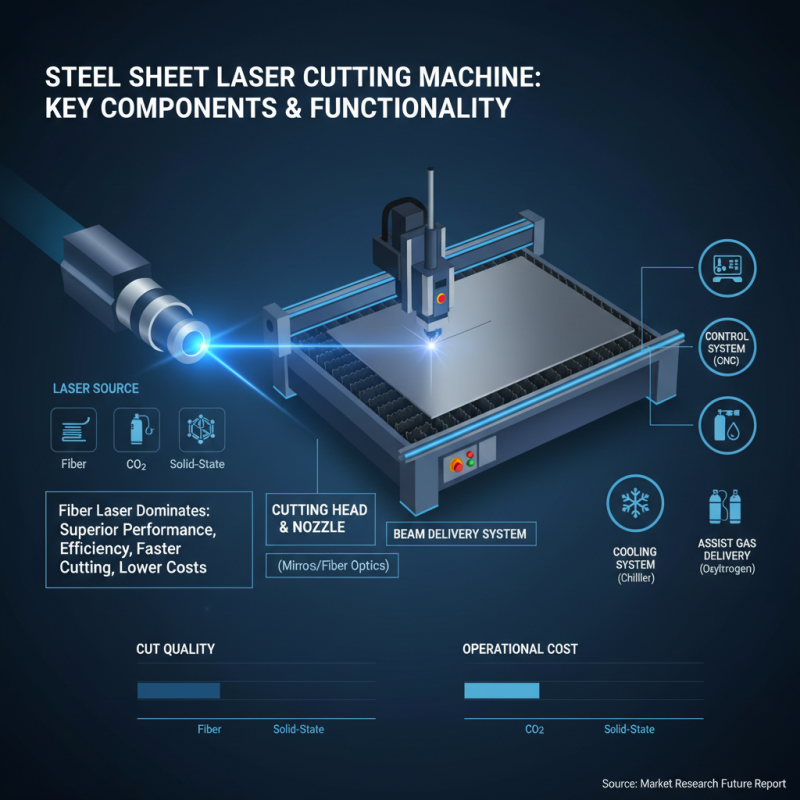
The core functionality of a steel sheet laser cutting machine is largely dependent on its key components, each playing a vital role in the overall performance of the system. At the heart of the machine is the laser source, which can be either fiber, CO2, or solid-state lasers. According to a report by Market Research Future, the fiber laser segment is expected to dominate the market due to its superior performance and efficiency, allowing for faster cutting speeds and lower operational costs. The choice of laser source directly impacts the quality of the cut, energy consumption, and maintenance requirements.
Another essential component is the CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system, which allows precise control over the cutting process. The advanced software integrated into these machines enables operators to define cutting paths with minute precision, optimizing the material usage and reducing waste. Recent industry studies indicate that automation, facilitated by advanced CNC controls, can enhance production efficiency by up to 30%. Furthermore, the cutting head, equipped with lenses and mirrors, focuses the laser beam onto the material, ensuring smooth edges and high-quality finishes. The integration of automated loading and unloading systems also streamlines the workflow, allowing for continuous operation and reduced turnaround times in high-demand manufacturing settings.
Laser cutting technology operates on the principle of directing a high-powered laser beam onto a material's surface, which is usually metal in the context of steel sheet cutting. The intense heat generated by the focused laser energy melts or vaporizes the material, allowing for precise cuts to be made. The process begins with the setup of the CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system, which allows operators to input designs and specifications for the desired cuts. This automation not only enhances the accuracy of the cuts but also significantly increases production efficiency.
As the laser beam interacts with the steel sheet, a stream of assist gas—commonly oxygen or nitrogen—is often used to enhance the cutting process. This gas helps to blow away the molten material, preventing any re-solidification and ensuring a clean edge. The versatility of laser cutting technology allows it to handle various thicknesses and types of steel, making it an ideal choice for numerous applications, from industrial manufacturing to artistic metalwork. The ability to maintain high precision while accommodating complex shapes sets laser cutting apart from traditional cutting methods, proving its significance in modern fabrication processes.
The process of steel sheet laser cutting is a precise and efficient method commonly used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Initially, the process begins with the preparation of the steel sheet, which is typically cleaned and positioned on a cutting table. This ensures that the surface is free from contaminants that may affect the cutting quality. According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the global laser cutting machine market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2020 to 2025, indicating the rising demand for advanced cutting technologies.
Once the steel sheet is properly set up, the laser cutting machine is calibrated for optimal performance. The laser beam, generated by a high-powered CO2 or fiber laser, is directed through a focusing lens to produce a concentrated spot of light on the steel surface. This intense heat melts or vaporizes the material, allowing for intricate designs and precise cuts. Studies have shown that laser cutting can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.1 mm, making it a preferred choice for detailed applications.
During the cutting process, an assist gas, such as oxygen or nitrogen, is often used to remove molten material and improve the quality of the cut edges. After the cutting operation is complete, the remnants of the steel sheet can either be recycled or repurposed, contributing to sustainability in manufacturing. As the industry shifts towards automation and improved efficiency, laser cutting technology will continue to play a critical role, supported by innovations in machine capabilities and software integration.
| Process Step | Description | Time (minutes) | Materials Cut |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Setting up the machine and loading the steel sheet. | 5 | Mild Steel, Stainless Steel |
| 2. Programming | Inputting cutting patterns and settings into the machine's software. | 10 | Aluminum, Copper |
| 3. Cutting | The laser cuts through the steel sheet according to programmed paths. | 15 | Mild Steel, Stainless Steel |
| 4. Inspection | Checking the quality of the cut and measuring dimensions. | 8 | All types |
| 5. Cleanup | Removing debris and preparing the machine for the next job. | 5 | All types |
Laser cutting technology has revolutionized the steel fabrication industry, offering precise and efficient methods for cutting, shaping, and engraving metal sheets. One of the primary applications of laser cutting in steel fabrication is its ability to produce intricate designs and complex geometries that traditional cutting methods often struggle to achieve. This ability to create highly detailed components has made laser cutting a preferred choice in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, where precision is paramount.
The benefits of laser cutting extend beyond design flexibility. The process is known for its speed and efficiency, significantly reducing production times while maintaining high quality. Additionally, laser cutting minimizes material waste, as it requires narrower kerf widths compared to traditional cutting techniques. This results in lower costs and a more sustainable approach to manufacturing.
**Tips:** When considering laser cutting for steel fabrication, ensure that you are familiar with the different types of steel available, as each may respond differently to laser cutting. Furthermore, optimizing the design for laser cutting can lead to enhanced results, focusing on factors like cutting speed, thickness, and part orientation to maximize efficiency.






By using this site you agree to the use of cookies by the company in accordance with the Privacy Policy
Have a questions or want to know more about our company? We'll be expecting you.
